Diagnosing Your WiFi Woes: Why is Your Signal Weak?
A slow or unreliable WiFi connection can be incredibly frustrating. Before diving into solutions, it's crucial to understand why your WiFi signal strength might be weak. Several factors can contribute to poor WiFi performance, including:
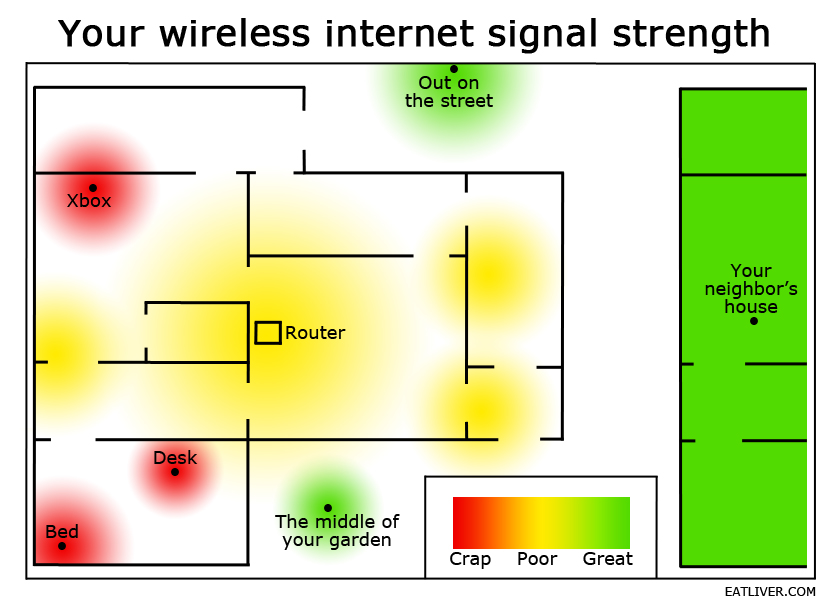
- Router Placement: The physical location of your router significantly impacts signal coverage. Walls, furniture, and even appliances can obstruct and weaken the signal.
- Router Interference: Other electronic devices, like microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth devices, can interfere with the WiFi signal.
- Router Age and Technology: Older routers may not support the latest WiFi standards, limiting their speed and range.
- Network Congestion: Too many devices connected to your WiFi network can strain the router's resources, leading to slower speeds for everyone.
- Distance from Router: The further you are from the router, the weaker the signal becomes.
- Building Materials: Certain building materials, such as concrete, metal, and plaster, can significantly block WiFi signals.
- Outdated Router Firmware: Like any software, router firmware needs to be updated regularly to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Neighboring WiFi Networks: In densely populated areas, overlapping WiFi channels from neighboring networks can cause interference.
By identifying the potential causes of your weak WiFi signal, you can focus on the most effective solutions.
Strategic Router Placement: Location, Location, Location
One of the simplest and most effective ways to improve WiFi signal strength is to optimize your router's placement. Consider these tips:
Elevate Your Router
WiFi signals radiate outwards and downwards. Placing your router on a high shelf or mounting it on a wall can improve coverage, especially on lower floors.
Centralize Your Router
Position your router in a central location within your home to ensure even coverage throughout the house. Avoid placing it in a corner or against an exterior wall.
Keep it Away from Obstacles
Avoid placing your router near walls, large metal objects (like refrigerators), aquariums, or other obstructions that can block or interfere with the signal. Keep it away from microwaves as well.
Consider the Layout of Your Home
Think about the areas where you use WiFi the most. Try to position your router closer to those areas to ensure a strong signal where you need it most. Experiment with different locations to find the optimal spot.
Upgrade Your Router: Is it Time for a New Model?
If your router is several years old, it might be time for an upgrade. Newer routers offer significant improvements in speed, range, and features. Consider these factors when choosing a new router:
WiFi Standards
Look for a router that supports the latest WiFi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) or Wi-Fi 6E. These standards offer faster speeds, improved efficiency, and better performance in congested environments.
Dual-Band or Tri-Band Routers
Dual-band routers operate on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds and less interference, while the 2.4 GHz band has a longer range. Tri-band routers add a second 5 GHz band for even more bandwidth. Choose a router that meets your needs.
MU-MIMO Technology
MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) technology allows the router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously, improving performance for homes with many connected devices.
Mesh WiFi Systems
For larger homes or homes with challenging layouts, a mesh WiFi system can provide seamless coverage throughout the entire house. Mesh systems use multiple nodes that work together to create a single, unified network.
Optimize Your Router Settings: Tweak for Better Performance
Your router's settings can have a significant impact on its performance. Here are some settings you can adjust to improve your WiFi signal strength:
Choose the Right WiFi Channel
WiFi routers operate on different channels. If multiple routers in your area are using the same channel, it can lead to interference. Use a WiFi analyzer app (available for smartphones and computers) to identify the least congested channel and switch your router to that channel.
Adjust the Channel Width
The channel width determines the amount of bandwidth available for your WiFi network. A wider channel width (e.g., 40 MHz or 80 MHz on the 5 GHz band) can provide faster speeds, but it can also be more susceptible to interference. Experiment with different channel widths to find the optimal setting for your environment.
Enable QoS (Quality of Service)
QoS allows you to prioritize certain types of traffic, such as video streaming or online gaming. By prioritizing important traffic, you can ensure a smoother and more responsive experience even when your network is under heavy load.
Update Router Firmware
Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates that improve performance, fix bugs, and enhance security. Check your router's manufacturer's website for the latest firmware updates and install them promptly.
Extend Your WiFi Range: Boosters and Repeaters
If you're struggling to get a strong WiFi signal in certain areas of your home, you can use WiFi extenders or repeaters to boost the signal. Here's what you need to know:
WiFi Extenders
WiFi extenders work by receiving the existing WiFi signal from your router and rebroadcasting it. This can effectively extend the range of your WiFi network, but it can also reduce the overall speed. Place the extender halfway between your router and the area where you need better coverage.
WiFi Repeaters
WiFi repeaters are similar to extenders, but they typically connect to your router wirelessly. This can make them easier to set up, but it can also introduce more latency. Consider the pros and cons of each before making a decision.
Powerline Adapters
Powerline adapters use your home's electrical wiring to transmit data. This can be a good option if you have trouble getting a strong WiFi signal through walls or floors. Simply plug one adapter into an electrical outlet near your router and another adapter into an outlet in the area where you need better coverage.
Managing Connected Devices: Reduce Network Congestion
Too many devices connected to your WiFi network can strain the router's resources and slow down your internet speed. Here are some tips for managing connected devices:
Disconnect Unused Devices
Disconnect devices that you're not actively using from your WiFi network. This will free up bandwidth for the devices that you are using.
Limit Bandwidth Usage
Some devices, such as streaming services and online games, can consume a lot of bandwidth. Limit the bandwidth usage of these devices when possible.
Use Wired Connections
For devices that require a stable and reliable connection, such as desktop computers and gaming consoles, consider using a wired Ethernet connection instead of WiFi. This will free up bandwidth on your WiFi network for other devices.
Addressing Interference: Minimizing External Disruptions
External factors can also interfere with your WiFi signal. Here's how to minimize interference:
Identify Sources of Interference
Common sources of interference include microwaves, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and other electronic devices. Try to identify any potential sources of interference near your router and move them away.
Change WiFi Channel (Again!)
As mentioned earlier, overlapping WiFi channels from neighboring networks can cause interference. Use a WiFi analyzer app to identify the least congested channel and switch your router to that channel. Monitor the channel regularly as neighbors add or change their own WiFi networks.
Consider 5 GHz Over 2.4 GHz
The 5 GHz band is less prone to interference than the 2.4 GHz band. If your devices support 5 GHz, try connecting to the 5 GHz network instead of the 2.4 GHz network.
