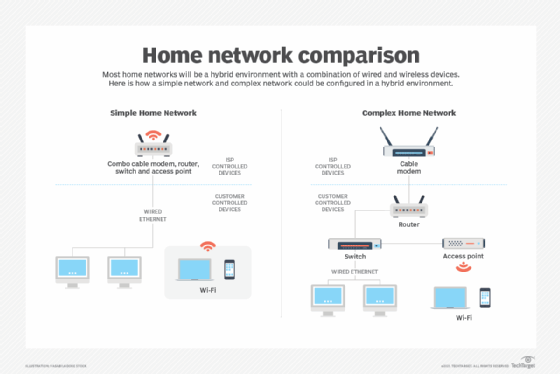
Introduction: Why You Need a Home Network
In today's digital age, a reliable home network is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and other internet-connected devices, a robust home network ensures seamless connectivity, efficient resource sharing, and enhanced entertainment options for everyone in your household. Setting up a home network allows you to share internet access, stream media, print documents, and even control smart home devices – all within the comfort of your own home.
Planning Your Home Network: Key Considerations
Before you dive into the technical aspects of setting up your home network, it's crucial to plan and consider a few key factors that will impact your network's performance and security.
1. Determine Your Network Needs
Start by identifying the number of devices that will be connected to your network simultaneously. Consider the bandwidth requirements of each device. Streaming high-definition videos, playing online games, and downloading large files all consume significant bandwidth. Understanding your usage patterns will help you choose the right internet plan and networking equipment.
2. Choose the Right Router
The router is the heart of your home network, responsible for directing traffic between your devices and the internet. When selecting a router, consider the following:
- Wireless Standards: Opt for a router that supports the latest Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), for faster speeds and improved performance.
- Frequency Bands: Dual-band routers operate on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies. The 2.4 GHz band offers wider coverage, while the 5 GHz band provides faster speeds and less interference. Tri-band routers offer an additional 5 GHz band for even better performance.
- Ports: Ensure the router has enough Ethernet ports to connect wired devices, such as desktop computers, gaming consoles, and smart TVs.
- Security Features: Look for routers with built-in firewalls, WPA3 encryption, and parental control features to protect your network from unauthorized access and malicious threats.
3. Consider Network Coverage
Assess the size and layout of your home to determine the optimal placement of your router. Walls, furniture, and other obstacles can interfere with Wi-Fi signals. If you have a large home or areas with weak Wi-Fi coverage, consider using a mesh Wi-Fi system or Wi-Fi extenders to expand your network's reach.
Setting Up Your Home Network: Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you've planned your home network, let's walk through the process of setting it up.
1. Connect Your Modem to the Router
First, connect your modem to the router using an Ethernet cable. Plug one end of the cable into the modem's Ethernet port and the other end into the router's WAN (Wide Area Network) or Internet port. Power on your modem and router, and wait for them to initialize.
2. Access the Router's Configuration Interface
To configure your router, you'll need to access its web-based configuration interface. This is typically done by typing the router's IP address into your web browser's address bar. The IP address is usually printed on the router's label or in the router's manual. Common IP addresses include 192.168.1.1, 192.168.0.1, and 10.0.0.1.
3. Configure Your Internet Connection
Once you've accessed the router's configuration interface, you'll need to configure your internet connection. Select the appropriate connection type (e.g., DHCP, PPPoE, Static IP) based on your internet service provider's (ISP) instructions. Enter any required credentials, such as your username and password.
4. Set Up Your Wireless Network
Next, configure your wireless network settings. Choose a strong and unique network name (SSID) and select a secure encryption protocol, such as WPA3. Create a strong password for your Wi-Fi network to prevent unauthorized access. You can also choose to hide your network name to make it less visible to others.
5. Connect Your Devices
Now that your router is configured, you can connect your devices to the network. For wireless devices, select your network name from the list of available networks and enter the Wi-Fi password. For wired devices, simply connect them to the router's Ethernet ports using Ethernet cables.
6. Configure IP Addresses (Optional)
By default, most routers use DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to automatically assign IP addresses to connected devices. However, you can also manually assign static IP addresses to specific devices if needed. This can be useful for devices that require a consistent IP address, such as network printers or servers.
Securing Your Home Network: Essential Practices
Securing your home network is crucial to protect your personal information and prevent unauthorized access. Here are some essential security practices to follow:
1. Change the Default Router Password
The default password for your router is often publicly available, making it vulnerable to attacks. Change the default password to a strong and unique password to prevent unauthorized access to your router's configuration interface.
2. Enable WPA3 Encryption
WPA3 is the latest and most secure Wi-Fi encryption protocol. Enable WPA3 encryption on your router to protect your wireless network from eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
3. Enable Firewall Protection
Most routers have a built-in firewall that helps protect your network from malicious threats. Enable the firewall to block unauthorized access attempts and prevent malicious software from entering your network.
4. Keep Your Router's Firmware Updated
Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to fix security vulnerabilities and improve performance. Keep your router's firmware up to date to ensure that your network is protected from the latest threats.
5. Use Strong Passwords
Use strong and unique passwords for all of your online accounts. Avoid using easily guessable passwords, such as your name, birthday, or address. Consider using a password manager to generate and store your passwords securely.
6. Enable Guest Network (Optional)
If you frequently have guests visiting your home, consider enabling a guest network. A guest network allows guests to access the internet without accessing your main network resources, such as your files and printers.
