Mastering Music Production: Essential Tips for Aspiring Producers
Embarking on the journey of music production can be both exhilarating and daunting. Whether you're crafting electronic beats, recording a live band, or composing orchestral scores, a solid foundation in production techniques is crucial. This guide provides essential tips to help you elevate your music production skills, covering everything from foundational knowledge to advanced techniques.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Before diving into complex techniques, it's vital to grasp the fundamentals of music production. This includes understanding audio principles, mastering the basics of your chosen DAW (Digital Audio Workstation), and developing a strong ear for music.
Choose the Right DAW
Your DAW is the heart of your music production setup. Popular options include Ableton Live, Logic Pro X, FL Studio, and Pro Tools. Each DAW has its strengths and weaknesses, so research and experiment to find the one that best suits your workflow and creative style. Consider factors like user interface, available plugins, and integration with hardware.
Learn Music Theory
While not strictly necessary, a basic understanding of music theory can significantly enhance your production capabilities. Knowledge of scales, chords, and harmony allows you to create more interesting and complex musical arrangements. There are numerous online resources and courses available to learn music theory at your own pace.
Train Your Ear
Developing a keen ear is essential for identifying frequencies, detecting subtle nuances in sound, and making informed mixing decisions. Practice ear training exercises regularly, focusing on identifying intervals, chords, and EQ frequencies. This will enable you to make more precise adjustments to your audio and create a more polished final product.
Optimizing Your Recording Process
The quality of your recordings directly impacts the overall quality of your music. Ensuring clean, well-recorded audio is paramount, regardless of the genre you're producing.
Invest in Quality Equipment
While you don't need the most expensive equipment to start, investing in a decent microphone, audio interface, and studio monitors is crucial. A good microphone captures clear and detailed audio, while a quality audio interface provides clean preamps and low latency for recording. Studio monitors provide an accurate representation of your audio, allowing you to make informed mixing decisions.
Proper Microphone Placement
Microphone placement can drastically affect the sound of your recordings. Experiment with different microphone positions to find the sweet spot for each instrument or vocal. Consider factors like proximity effect (the increase in bass frequencies as the microphone gets closer to the sound source) and off-axis coloration (the change in sound quality as the microphone is positioned off-center). Common microphone techniques include the XY stereo technique, the ORTF stereo technique, and the Mid-Side (M/S) stereo technique.
Control Your Recording Environment
The acoustics of your recording environment play a significant role in the quality of your recordings. Minimize unwanted reflections and reverberation by treating your room with acoustic panels, bass traps, and diffusers. Even simple measures like hanging thick curtains or using blankets can significantly improve your room's acoustics.
Mastering Mixing Techniques
Mixing is the process of blending individual tracks together to create a cohesive and balanced sonic landscape. It involves adjusting levels, EQ, compression, and other effects to shape the sound of each track and create a pleasing overall mix.
Gain Staging
Proper gain staging is essential for achieving a clean and dynamic mix. Ensure that your audio signals are not clipping (exceeding the maximum level) at any point in the signal chain. Aim for a healthy signal level without pushing your tracks too hard. This provides headroom for mixing and mastering.
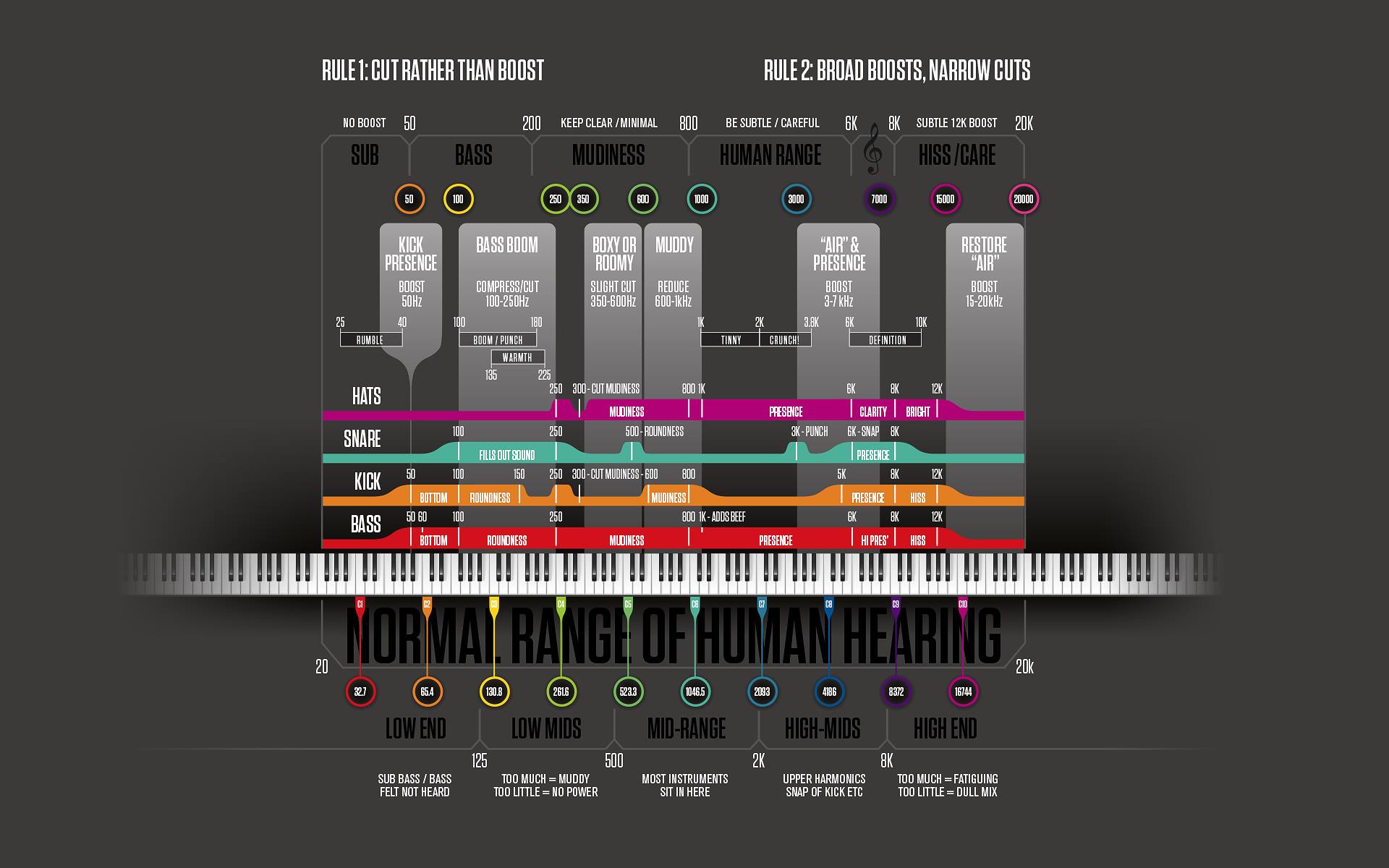
Equalization (EQ)
EQ is used to shape the tonal balance of individual tracks. Use EQ to remove unwanted frequencies, enhance desirable frequencies, and create separation between instruments in the mix. Common EQ techniques include high-pass filtering (removing low frequencies), low-pass filtering (removing high frequencies), and boosting or cutting specific frequency ranges. Remember to use EQ subtly and avoid over-processing.
Compression
Compression reduces the dynamic range of a signal, making it sound louder and more consistent. It can be used to add punch to drums, smooth out vocals, and glue the mix together. Experiment with different compressor settings, such as threshold, ratio, attack, and release, to achieve the desired effect. Be careful not to over-compress your audio, as this can result in a flat and lifeless sound.
Reverb and Delay
Reverb and delay add depth and space to your mix. Use reverb to simulate the acoustics of different environments, such as a small room or a large hall. Use delay to create rhythmic echoes or add subtle ambience. Experiment with different reverb and delay types, such as plate reverb, hall reverb, and tape delay, to find the sounds that best suit your music.
Panning
Panning involves positioning sounds in the stereo field. Use panning to create a wider and more immersive soundscape. Pan different instruments to different positions in the stereo field to create separation and prevent the mix from sounding cluttered. Consider the placement of each instrument in the mix and how it contributes to the overall stereo image.
Harnessing the Power of Plugins
Plugins are software tools that extend the functionality of your DAW. They can be used for a wide range of tasks, including EQ, compression, reverb, delay, synthesis, and mastering.
Explore Different Plugin Types
There are countless plugins available, each with its unique strengths and weaknesses. Experiment with different plugin types to find the tools that best suit your workflow and creative style. Consider investing in high-quality plugins from reputable developers.
Learn Plugin Workflow and Features
Each plugin has its own unique interface and set of parameters. Take the time to learn the ins and outs of each plugin before using it in your productions. Watch tutorials, read manuals, and experiment with different settings to understand how each parameter affects the sound.
Use Plugins Subtly and Intentionally
Plugins are powerful tools, but they should be used subtly and intentionally. Avoid over-processing your audio with excessive EQ, compression, or other effects. Always listen critically and make adjustments based on what you hear, not just what you see on the screen.
The Art of Arrangement
Arrangement is the process of structuring your song and creating a compelling narrative. A well-arranged song keeps the listener engaged and interested from beginning to end.
Build a Strong Foundation
Start with a strong foundation, such as a catchy hook, a memorable melody, or a compelling rhythm. Build your arrangement around this foundation, adding and subtracting elements to create a dynamic and engaging listening experience.
Create Variety and Dynamics
Avoid repetition and monotony by creating variety and dynamics in your arrangement. Introduce new elements gradually, and create moments of tension and release to keep the listener engaged. Use automation to create subtle changes in volume, panning, and other parameters to add movement and interest to your arrangement.
Pay Attention to Transitions
Transitions are the glue that holds your arrangement together. Use transitions to smoothly connect different sections of your song and create a seamless flow. Common transition techniques include using fills, sweeps, and fades.
Mastering for the Final Polish
Mastering is the final stage of the music production process, where the overall sound of your tracks is refined and optimized for distribution. Mastering involves adjusting the overall loudness, EQ, and dynamics of your tracks to ensure they sound their best on all playback systems.
Gain an Understanding of Mastering Principles
Mastering requires a different skillset than mixing. Understanding concepts like perceived loudness, dynamic range and inter-sample peaks is important. Also, understanding loudness standards for different platforms (Spotify, Apple Music, etc.) is crucial.
Consider Professional Mastering
While it's possible to master your own music, consider hiring a professional mastering engineer for the best results. Mastering engineers have specialized equipment, a trained ear, and experience working with a wide range of genres. They can provide an objective perspective on your music and help you achieve a polished and professional sound.
