Understanding the Importance of Online Data Protection
In today's digital age, our lives are increasingly intertwined with the internet. We share personal information, financial details, and sensitive data online every day. This makes protecting your data online more crucial than ever. With the rise of cyber threats, data breaches, and identity theft, understanding and implementing robust online security measures is no longer optional; it's a necessity. This guide will provide you with actionable steps you can take to safeguard your information and maintain your online privacy. Your data is valuable, and protecting it should be a top priority.
Strengthening Your Passwords
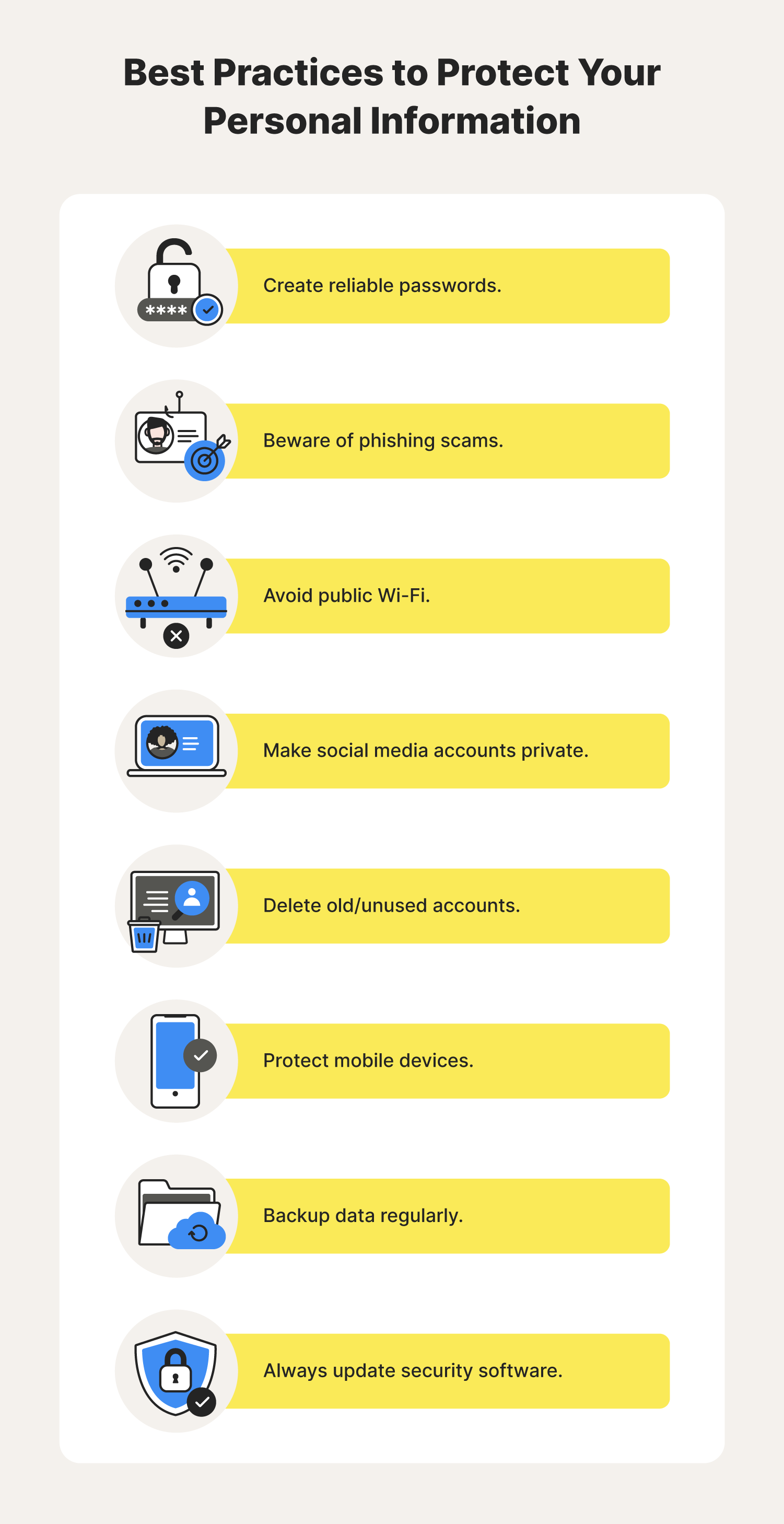
Your passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access to your accounts and data. Weak or easily guessable passwords are a major vulnerability that cybercriminals can exploit. Here’s how to create and manage strong passwords:
Creating Strong Passwords
A strong password should be:
- Long: Aim for at least 12 characters. The longer, the better.
- Complex: Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Unique: Don't reuse the same password for multiple accounts.
- Unpredictable: Avoid using personal information like your name, birthdate, or pet's name.
Consider using a password generator to create strong, random passwords. These tools can generate complex passwords that are difficult to crack.
Password Managers
Remembering numerous complex passwords can be challenging. A password manager can securely store and manage your passwords. These tools also offer features like:
- Password generation
- Automatic form filling
- Secure password storage
- Password breach monitoring
Popular password managers include LastPass, 1Password, and Dashlane. Choose a reputable password manager with strong security features and a proven track record.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts. Even if someone manages to obtain your password, they will need a second factor to access your account. Common 2FA methods include:
- SMS codes: A code is sent to your phone via text message.
- Authenticator apps: Apps like Google Authenticator or Authy generate time-based codes.
- Hardware security keys: Physical keys like YubiKey provide the strongest level of security.
Enable 2FA on all accounts that offer it, especially your email, banking, and social media accounts. This simple step can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Securing Your Devices
Your devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets, are gateways to your online data. Securing these devices is essential for protecting your information.
Software Updates
Regularly updating your operating system and software is crucial for security. Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Enable automatic updates to ensure you always have the latest security protections. This includes updating your web browser, antivirus software, and any other applications you use regularly.
Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software on all your devices. These programs can detect and remove malicious software, such as viruses, spyware, and ransomware. Keep your antivirus software up to date to ensure it can protect against the latest threats. Consider using real-time scanning features to continuously monitor your system for suspicious activity.
Firewalls
A firewall acts as a barrier between your device and the internet, blocking unauthorized access. Most operating systems have built-in firewalls. Make sure your firewall is enabled and configured correctly. You can also use hardware firewalls, which are separate devices that provide additional security for your network.
Device Encryption
Encrypting your devices protects your data even if they are lost or stolen. Encryption scrambles your data, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. Most operating systems offer built-in encryption features, such as BitLocker for Windows and FileVault for macOS. Enable encryption on all your devices, including your smartphones and tablets.
Protecting Your Network
Your home network is another potential entry point for cybercriminals. Securing your network is essential for protecting all the devices connected to it.
Secure Your Wi-Fi Router
Your Wi-Fi router is the gateway to your home network. Secure it with a strong password and enable WPA3 encryption, the latest and most secure Wi-Fi security protocol. Change the default router password to a strong, unique password. Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup), a feature that can be vulnerable to attacks. Regularly update your router's firmware to patch any security vulnerabilities.
Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, protecting your data from eavesdropping. Use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, such as those at coffee shops or airports. A VPN can also help you bypass geo-restrictions and access content that is not available in your region. Choose a reputable VPN provider with a strong privacy policy and a proven track record.
Be Careful with Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them vulnerable to eavesdropping. Avoid transmitting sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details, over public Wi-Fi. If you must use public Wi-Fi, use a VPN to encrypt your traffic. Be wary of fake Wi-Fi hotspots that are set up by cybercriminals to steal your data.
Practicing Safe Browsing Habits
Your browsing habits can significantly impact your online security. Practicing safe browsing habits can help you avoid malware, phishing scams, and other online threats.
Be Wary of Phishing Emails and Websites
Phishing is a type of cyber attack that uses deceptive emails or websites to trick you into revealing your personal information. Be wary of emails or websites that ask for your personal information, especially your passwords or financial details. Check the sender's email address carefully and look for grammatical errors or other red flags. Never click on links or download attachments from suspicious emails. Verify the authenticity of websites by checking the URL and looking for the padlock icon in the address bar.
Avoid Suspicious Links and Downloads
Be cautious about clicking on links or downloading files from unknown sources. These links and files may contain malware or other malicious software. Only download software from reputable sources, such as the official website of the software vendor. Scan downloaded files with antivirus software before opening them.
Use a Secure Browser
Choose a web browser that prioritizes security and privacy. Popular secure browsers include Firefox, Chrome, and Brave. Configure your browser settings to block pop-ups, cookies, and other tracking technologies. Use browser extensions that enhance your security and privacy, such as ad blockers and privacy protectors.
Managing Your Privacy Settings
Many online services collect and share your personal information. Managing your privacy settings can help you control how your data is used and shared.
Review Privacy Settings on Social Media
Social media platforms collect a vast amount of data about you, including your posts, photos, and contacts. Review your privacy settings on social media platforms to limit the amount of information you share publicly. Adjust your settings to control who can see your posts, who can tag you in photos, and who can contact you. Be mindful of the information you share on social media, as it can be used for targeted advertising or even identity theft.
Limit Data Sharing with Third-Party Apps
Many apps request access to your personal information, such as your contacts, location, and photos. Review the permissions requested by apps before installing them. Only grant permissions that are necessary for the app to function. Be wary of apps that request excessive permissions, as they may be collecting your data for malicious purposes. Regularly review and revoke permissions for apps that you no longer use.
Use Privacy-Focused Search Engines
Search engines like Google and Bing track your search history and use it to personalize your search results and display targeted ads. Consider using privacy-focused search engines like DuckDuckGo, which do not track your searches or collect your personal information. These search engines provide unbiased search results without compromising your privacy.
