Understanding the Threat Landscape: Viruses and Malware
In today's digital age, our computers are constantly under threat from malicious software, commonly known as viruses and malware. Understanding what these threats are and how they work is the first step in protecting your valuable data and maintaining a secure online experience. Malware is a broad term encompassing various types of malicious software designed to infiltrate and damage computer systems. Viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware all fall under the malware umbrella, each with its own unique method of infection and harmful effects.
What is a Virus?
A computer virus is a type of malware that replicates itself by inserting its code into other programs or files. When an infected program is executed, the virus spreads, infecting other files and potentially causing data corruption, system instability, or even complete system failure. Viruses often rely on user interaction, such as opening an infected email attachment or running a compromised program, to spread.
What is Malware?
Malware, short for malicious software, is a more encompassing term that includes various types of harmful programs designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Besides viruses, common types of malware include:
- Worms: These are self-replicating programs that can spread across networks without human interaction, exploiting vulnerabilities in software to infect other systems.
- Trojans: Disguised as legitimate software, Trojans trick users into installing them, often containing hidden malicious code that can steal data, install other malware, or grant remote access to attackers.
- Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts a victim's files and demands a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. Ransomware attacks can be devastating, leading to significant financial losses and data breaches.
- Spyware: Spyware secretly monitors user activity, collecting sensitive information such as passwords, browsing history, and credit card details, which is then transmitted to attackers.
- Adware: While often less harmful than other types of malware, adware can be annoying and intrusive, displaying unwanted advertisements and potentially redirecting users to malicious websites.
Essential Software for Computer Protection
Having the right software is crucial for protecting your computer from viruses and malware. The following are essential tools that should be installed and regularly updated:
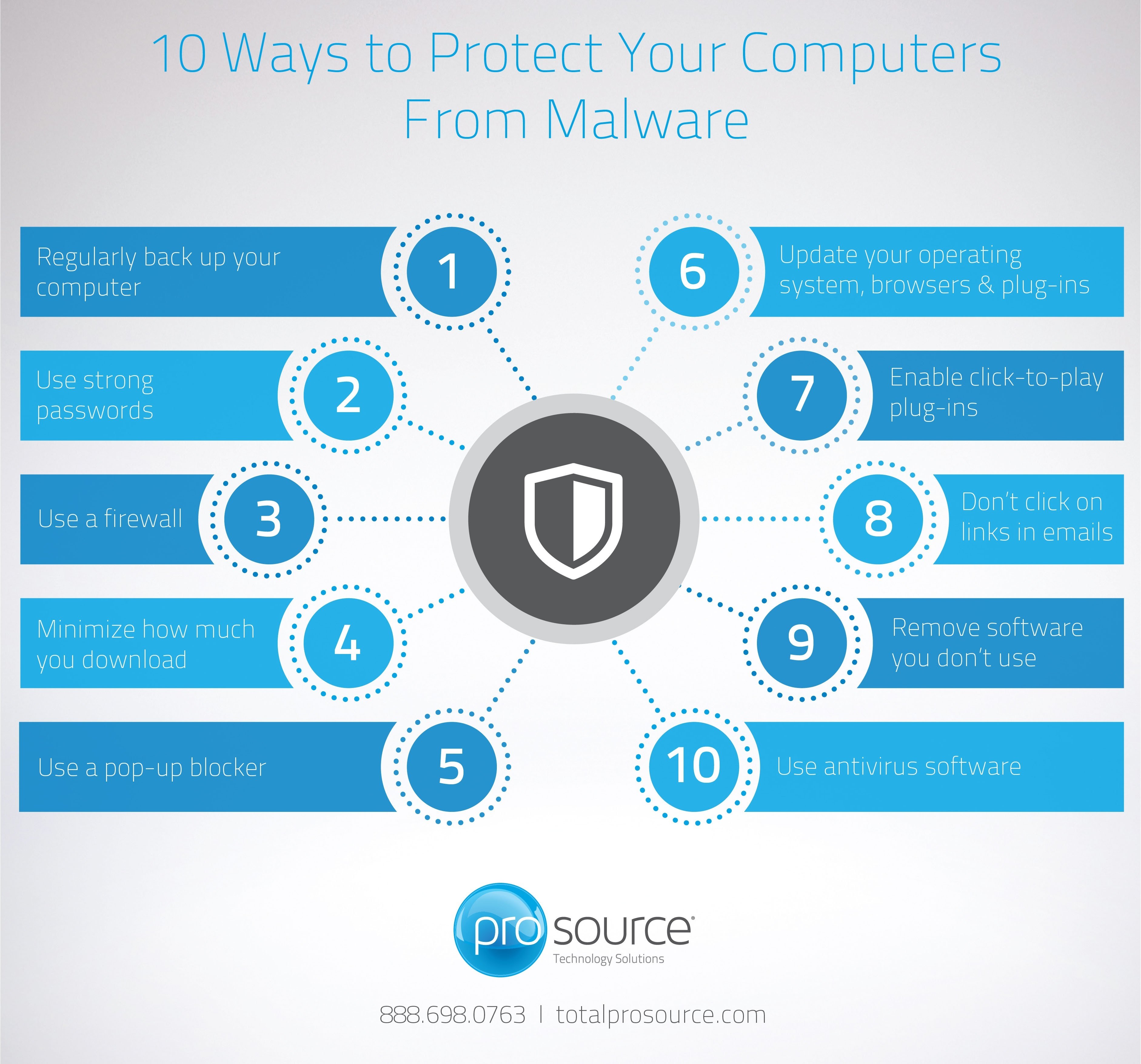
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software is your first line of defense against malware. It scans your computer for known viruses, worms, Trojans, and other threats, and removes or quarantines them. Modern antivirus programs also offer real-time protection, monitoring system activity and blocking malicious code from executing. Choose a reputable antivirus program from a well-known vendor and ensure that it's always up-to-date with the latest virus definitions. Popular options include:
- Norton Antivirus
- McAfee Total Protection
- Bitdefender Total Security
- Kaspersky Internet Security
- Avast Free Antivirus (for basic protection)
Firewall
A firewall acts as a barrier between your computer and the outside world, controlling network traffic and blocking unauthorized access. Most operating systems come with a built-in firewall, but you can also install a dedicated firewall program for enhanced protection. Configure your firewall to allow only necessary network connections and block any suspicious traffic.
Anti-Malware Software
While antivirus software focuses primarily on viruses, anti-malware software provides broader protection against a wider range of threats, including spyware, adware, and potentially unwanted programs (PUPs). Consider installing a dedicated anti-malware program in addition to your antivirus software for comprehensive protection. Malwarebytes is a popular and effective anti-malware solution.
Safe Browsing Habits: Your First Line of Defense
Software is important, but your own behavior is just as critical when it comes to protecting your computer from viruses and malware. Practicing safe browsing habits is essential for minimizing your risk of infection.
Be Wary of Suspicious Emails
Email is a common vector for malware attacks. Be cautious of emails from unknown senders, especially those containing attachments or links. Never open attachments or click on links in emails from untrusted sources, as they may contain malicious code. Even if an email appears to be from a legitimate source, such as your bank or a social media platform, double-check the sender's address and be wary of requests for personal information.
Download Software from Official Sources
Always download software from official websites or trusted app stores. Avoid downloading programs from third-party websites or file-sharing networks, as they may contain malware. Before installing any software, read the reviews and check the publisher's reputation. Pay attention to the installation process and deselect any bundled software or unwanted programs.
Keep Your Software Up-to-Date
Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malware. Enable automatic updates for your operating system, web browser, and other applications to ensure that you're always running the latest versions with the most recent security fixes. Regularly check for updates manually if automatic updates are not enabled.
Use Strong Passwords
Weak passwords are easy to crack, making your accounts vulnerable to hackers. Use strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information, such as your name, birthday, or pet's name. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords.
Be Careful What You Click On
Exercise caution when clicking on links, especially on social media or in online advertisements. Malicious websites often masquerade as legitimate sites to trick users into entering their personal information or downloading malware. Before clicking on a link, hover your mouse over it to see the actual URL and make sure it's a trusted website.
Regular System Maintenance: Keeping Your Computer Healthy
Regular system maintenance is essential for maintaining the overall health and security of your computer. Performing these tasks regularly can help prevent malware infections and improve system performance.
Run Regular Scans with Your Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Schedule regular scans with your antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and remove any hidden threats. Consider running a full system scan at least once a week. Also, run a scan whenever you suspect that your computer may be infected.
Back Up Your Data Regularly
Backing up your data is crucial in case of a malware infection or other data loss event. Regularly back up your important files and documents to an external hard drive, cloud storage, or other secure location. That way, if your computer is compromised, you can restore your data without losing valuable information.
Keep Your Hard Drive Clean
A cluttered hard drive can slow down your computer and make it more vulnerable to malware. Regularly delete unnecessary files, uninstall unused programs, and defragment your hard drive to optimize system performance. Use a disk cleanup utility to remove temporary files and other junk data.
Monitor System Performance
Pay attention to your computer's performance. If you notice any unusual behavior, such as slow performance, frequent crashes, or strange error messages, it could be a sign of a malware infection. Run a scan with your antivirus and anti-malware software to investigate.
Advanced Protection Techniques: Going the Extra Mile
For users who want to take their computer security to the next level, there are several advanced protection techniques that can be implemented.
Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, masking your IP address and protecting your online privacy. Using a VPN can help prevent hackers from intercepting your data and tracking your online activity. It's especially useful when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are often unsecured.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts by requiring a second verification code in addition to your password. This code is typically sent to your phone or generated by an authenticator app. Even if someone manages to steal your password, they won't be able to access your account without the second verification code.
Use a Password Manager
A password manager securely stores your passwords and automatically fills them in when you visit websites. This makes it easier to use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts without having to remember them all. Most password managers also offer features such as password generation and security audits.
Consider Using a Linux-Based Operating System
Linux-based operating systems are generally considered to be more secure than Windows or macOS, due to their open-source nature and robust security features. While switching to Linux may require some technical expertise, it can significantly reduce your risk of malware infections.
